Understanding your role as a tutor is crucial to effectively support your students and foster their academic growth. Whether you’re new to tutoring or seeking to enhance your current approach, knowing what is my role as a tutor helps you navigate the responsibilities and expectations that come with this vital position.
Why Knowing Your Role Matters
Grasping the role of a tutor goes beyond simply helping students with their homework. It encompasses a range of responsibilities that contribute to a student’s overall learning experience. By clearly defining tutor responsibilities, you can create a structured and supportive environment that promotes not only academic success but also personal development for your students.
Understanding the Role of a Tutor
To fully comprehend what is my role as a tutor, it’s essential to break down the various components that define tutoring.
Defining Tutoring
Tutoring is a personalized educational support system aimed at enhancing a student’s understanding and performance in specific subjects or skills. Unlike conventional classroom settings, tutoring offers one-on-one or small group interactions, allowing for tailored instruction that addresses individual student needs.
Different Types of Tutoring
- Academic Tutoring
- Focuses on subjects like mathematics, science, language arts, and history.
- Helps students improve grades and comprehend complex concepts.
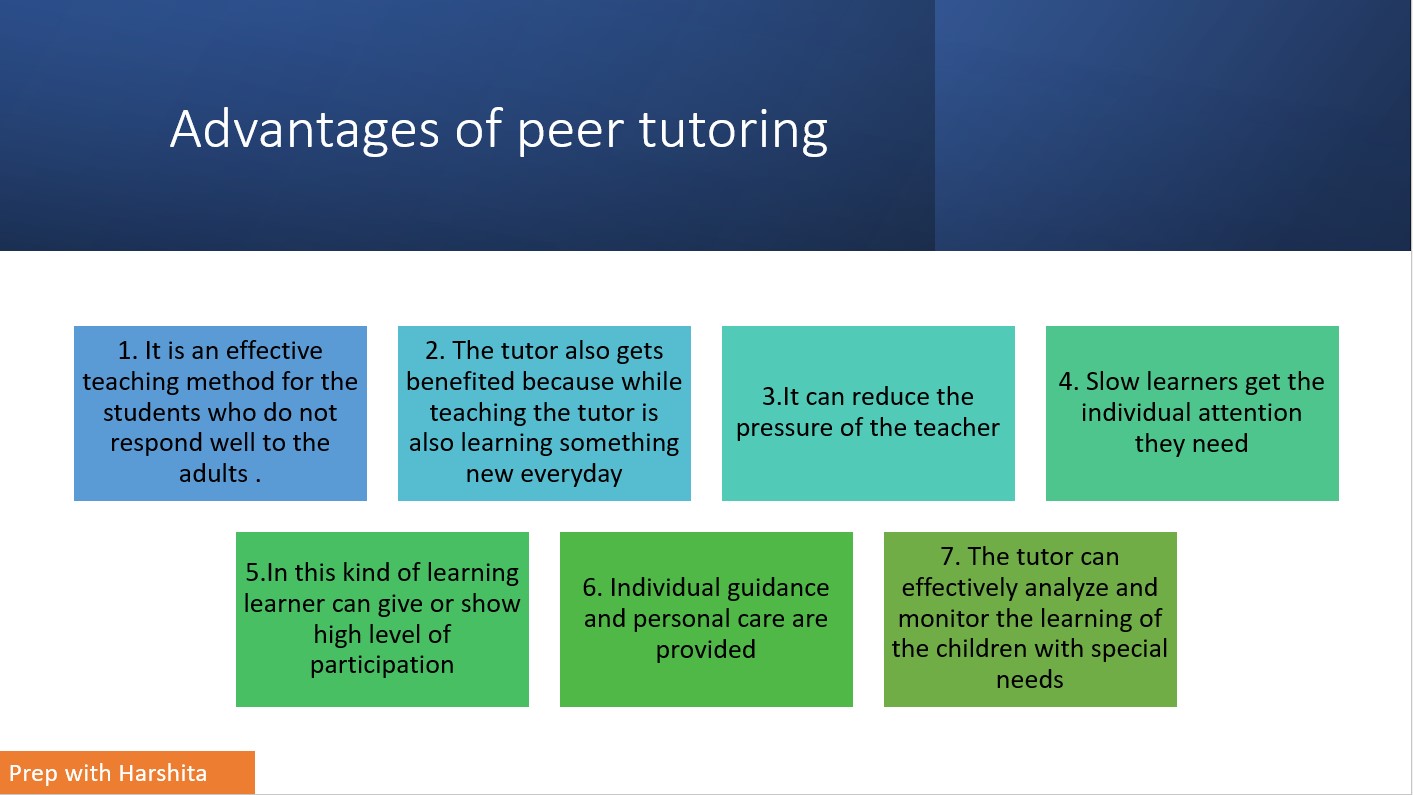
- Peer Tutoring
- Involves students helping each other under supervision.
- Encourages collaborative learning and reinforces the tutor’s own knowledge.
- Online Tutoring
- Conducted through digital platforms.
- Offers flexibility in scheduling and access to a wider range of resources.
- Test Preparation Tutoring
- Prepares students for standardized tests such as SAT, ACT, or GRE.
- Focuses on test-taking strategies and practice exams.
The Goal of Tutoring Sessions
The primary objective of tutoring is to facilitate a deeper understanding of the subject matter, build confidence, and develop effective learning strategies. By addressing specific challenges and reinforcing strengths, tutors help students achieve their academic goals and foster a lifelong love for learning.
Key Responsibilities of a Tutor
Understanding tutor responsibilities is crucial for anyone stepping into this role. These responsibilities ensure that tutoring sessions are effective, structured, and beneficial for the student.
- Preparing Lesson Plans
- Develop structured plans tailored to the student’s needs.
- Incorporate various teaching methods and materials to enhance learning.
- Assessing Student Needs
- Conduct initial assessments to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
- Continuously evaluate progress and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Teaching and Explaining Concepts
- Break down complex ideas into understandable parts.
- Use examples, analogies, and practical applications to clarify topics.
- Providing Feedback and Monitoring Progress
- Offer constructive feedback to guide the student’s improvement.
- Track academic performance and adjust tutoring methods as needed.
- Creating a Positive Learning Environment
- Foster a supportive and encouraging atmosphere.
- Encourage questions and active participation.
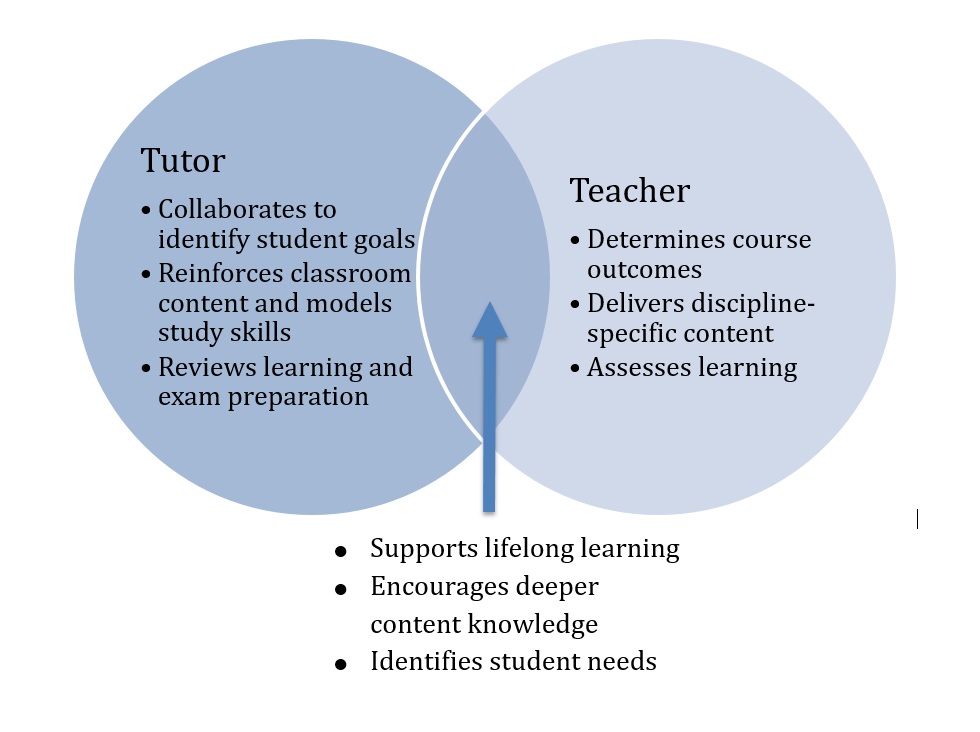
Differences Between Tutoring and Teaching
While both tutoring and teaching aim to educate, they differ in several key aspects. Understanding these differences can help tutors tailor their approach to better suit their roles.
| Aspect | Tutoring | Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Setting | One-on-one or small groups | Large classrooms with many students |
| Focus | Personalized attention and specific needs | Broad curriculum covering various topics |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to student’s pace and style | Structured schedule and standardized methods |
| Interaction | Interactive and conversational | Often lecture-based with limited interaction |
| Assessment | Continuous and informal | Periodic and formal assessments |
| Objective | Enhance understanding and address gaps | Deliver comprehensive education to all students |
Personalized Attention vs. Group Instruction
Tutors provide personalized attention, allowing them to focus on the unique challenges and learning styles of each student. This contrasts with group instruction, where teachers must cater to the collective needs of the entire class, often limiting the depth of individual support.
Flexibility in Teaching Methods
Tutoring offers greater flexibility in teaching methods. Tutors can experiment with different approaches, such as interactive activities, multimedia resources, and hands-on exercises, to find what best resonates with the student. In contrast, traditional teaching methods are often constrained by curriculum requirements and standardized testing.
Case Study: Effective Tutoring in Action
Maria’s Math Improvement
Maria, a high school sophomore, struggled with algebra and was on the verge of failing her class. Her parents decided to hire a tutor to help her overcome these challenges.
Tutor’s Approach:
- Initial Assessment: The tutor identified Maria’s weak points, including understanding variables and solving equations.
- Customized Lesson Plans: Created lessons that incorporated real-life examples to explain abstract concepts.
- Interactive Sessions: Used visual aids and interactive problem-solving techniques to engage Maria.
- Continuous Feedback: Provided regular feedback and celebrated small victories to build Maria’s confidence.
Within a semester, Maria’s grades improved from a C to an A in algebra. More importantly, she developed a stronger interest in mathematics and gained the confidence to tackle more challenging subjects.

The Importance of a Tutor’s Role
Understanding what is my role as a tutor extends beyond the basic functions of teaching and assisting with homework. A tutor plays a pivotal role in a student’s academic and personal development.
Supporting Student Learning
A tutor’s primary responsibility is to support student learning by enhancing their understanding of subject matter and improving their academic performance. This support manifests in several key ways:
- Enhancing Understanding of Subjects
- Clarifying Complex Concepts: Tutors break down difficult topics into manageable parts, making them easier to comprehend.
- Providing Additional Resources: They supply supplementary materials such as practice problems, reading materials, and multimedia resources to reinforce learning.
- Bridging Gaps in Knowledge
- Identifying Weak Areas: Through assessments and observations, tutors pinpoint areas where students struggle.
- Targeted Interventions: They design specific exercises and lessons to address these gaps, ensuring a more comprehensive understanding of the subject.
- Reinforcing Classroom Learning
- Supplementary Instruction: Tutors reinforce what is taught in school, providing additional explanations and examples.
- Homework Assistance: They help students complete assignments effectively, ensuring that homework serves as a learning tool rather than a source of frustration.
- Encouraging Critical Thinking
- Problem-Solving Skills: Tutors engage students in activities that promote analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
- Independent Learning: They encourage students to develop strategies for learning independently, fostering long-term academic success.
Case Study: Enhancing Understanding through Personalized Support
John’s Journey in Chemistry
John, a high school junior, was struggling with chemistry, particularly with understanding chemical reactions and equations. His chemistry teacher recommended he seek tutoring to improve his grasp of the subject.
Tutor’s Approach:
- Initial Assessment: The tutor conducted a diagnostic test to identify John’s specific areas of difficulty.
- Customized Lessons: Developed lesson plans that included hands-on experiments and real-life applications of chemical reactions.
- Interactive Learning: Utilized visual aids and interactive simulations to make abstract concepts more tangible.
Within three months, John’s grades in chemistry improved from a D to a B. More importantly, his enthusiasm for the subject grew, leading him to pursue advanced chemistry courses in subsequent years.
Building Confidence and Motivation
A tutor’s role is not limited to academic support; they also play a crucial part in building a student’s confidence and motivation. This emotional and psychological support is essential for a student’s overall development and academic success.
- Encouraging Students to Take Initiative
- Empowering Ownership: Tutors encourage students to take responsibility for their own learning, fostering a sense of ownership and independence.
- Setting Personal Goals: They help students set achievable goals, providing a clear direction and purpose for their studies.
- Building Self-Esteem Through Success
- Celebrating Achievements: Acknowledging and celebrating small victories boosts a student’s self-esteem and reinforces positive behavior.
- Positive Reinforcement: Providing consistent positive feedback helps students recognize their progress and capabilities.
- Motivating Students to Achieve Their Goals
- Intrinsic Motivation: Tutors inspire students to find personal reasons for wanting to succeed, making motivation more sustainable.
- Overcoming Obstacles: They teach resilience and strategies to overcome academic challenges, ensuring students remain motivated despite setbacks.
Fact: According to a study by the National Tutoring Association, students who receive regular tutoring are 55% more likely to experience improved academic performance and increased self-confidence compared to their peers who do not receive tutoring.
Personalized Learning Approaches
One of the most significant advantages of tutoring is the ability to personalize learning approaches to fit each student’s unique needs and learning style. Personalized tutoring ensures that instruction is tailored, effective, and engaging.
- Tailoring Lessons to Individual Learning Styles
- Visual Learners: Incorporating diagrams, charts, and visual aids to help visual learners grasp concepts.
- Auditory Learners: Utilizing discussions, verbal explanations, and auditory resources for those who learn best through listening.
- Kinesthetic Learners: Engaging in hands-on activities and experiments for students who learn through doing.
- Adapting to Different Paces of Learning
- Flexible Scheduling: Adjusting the pace of lessons based on the student’s comprehension and comfort level.
- Progress Monitoring: Continuously assessing progress and making necessary adjustments to the learning plan.
- Creating Customized Study Plans
- Individualized Goals: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals tailored to each student.
- Resource Allocation: Selecting appropriate materials and resources that align with the student’s learning objectives and preferences.
Matching Learning Styles with Tutoring Techniques
| Learning Style | Tutoring Technique | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Visual | Use of visual aids and graphic organizers | Diagrams, charts, mind maps |
| Auditory | Incorporate discussions and verbal explanations | Storytelling, lectures, audio recordings |
| Kinesthetic | Engage in hands-on activities and interactive exercises | Experiments, role-playing, interactive simulations |
Case Study: Personalized Learning for Enhanced Engagement
Sophia’s Success in History
Sophia, a high school student, found history classes monotonous and struggled to retain information. Her tutor identified her as an auditory learner and adapted her tutoring sessions accordingly.
Tutor’s Approach:
- Interactive Storytelling: Presented historical events through engaging narratives and discussions.
- Audio Resources: Utilized podcasts and audiobooks related to historical topics.
- Debates and Discussions: Encouraged Sophia to participate in debates, enhancing her understanding and retention of historical facts.
Sophia’s interest in history surged, leading to a significant improvement in her grades from a C to an A-. She developed a deeper appreciation for the subject and became more enthusiastic about learning.
Essential Skills for a Tutor
To excel in your role as a tutor, it’s essential to possess a diverse set of skills that enable you to effectively support and guide your students. Understanding what is my role as a tutor involves not only recognizing your responsibilities but also honing the skills that make your tutoring sessions impactful and successful.
Subject Matter Expertise
One of the foundational aspects of being a tutor is having a strong grasp of the subject matter you are teaching. Subject matter expertise ensures that you can provide accurate information, answer questions confidently, and create meaningful learning experiences for your students.
- Deep Knowledge in Specific Subjects
- Mastery of Content: A tutor must have a thorough understanding of the subjects they teach, including current theories, concepts, and methodologies.
- Staying Updated: Regularly updating your knowledge to stay abreast of the latest developments and changes in the subject area is crucial.
- Continuous Learning and Professional Development
- Pursuing Further Education: Engaging in ongoing education, such as attending workshops, seminars, and courses, helps maintain and enhance your expertise.
- Certifications and Specializations: Obtaining relevant certifications can bolster your credibility and demonstrate your commitment to excellence in tutoring.
Fact: Tutors with strong subject matter expertise are 65% more likely to help students achieve their academic goals compared to those with limited knowledge in the subject area.
Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are paramount for tutors. They enable you to convey information clearly, listen actively, and build strong relationships with your students.
- Clear and Effective Communication
- Simplifying Complex Concepts: The ability to break down intricate ideas into understandable terms is essential for student comprehension.
- Structured Explanations: Organizing information logically helps students follow and retain what they learn.
- Active Listening
- Understanding Student Needs: Listening attentively allows you to grasp the specific challenges and questions your students have.
- Responding Appropriately: Providing thoughtful and relevant responses based on what you hear fosters a supportive learning environment.
- Explaining Complex Concepts Simply
- Using Analogies and Examples: Relating new information to familiar concepts makes it easier for students to grasp difficult topics.
- Visual Aids and Demonstrations: Incorporating visual elements can enhance understanding and retention of information.
Case Study: Enhancing Communication for Better Understanding
Emma’s Struggle with Physics
Emma, a high school student, found physics particularly challenging, especially the concepts of force and motion. Her tutor recognized that Emma was overwhelmed by the technical jargon and abstract theories.
Tutor’s Approach:
- Simplified Explanations: The tutor used everyday examples, such as comparing force to pushing a shopping cart, to illustrate abstract concepts.
- Visual Aids: Diagrams and animations were employed to demonstrate how force and motion interact in different scenarios.
- Interactive Discussions: Encouraged Emma to ask questions and express her thoughts, ensuring she felt heard and understood.
Emma’s confidence in physics grew significantly. Her ability to understand and apply the concepts improved, leading to a noticeable increase in her grades from a C to an A- over the course of the semester.
Patience and Empathy
Patience and empathy are critical traits for tutors, as they create a nurturing and supportive learning environment where students feel comfortable expressing their difficulties and striving for improvement.
- Understanding Student Frustrations
- Recognizing Emotional States: Being attuned to a student’s feelings and frustrations helps in addressing their emotional needs alongside academic challenges.
- Providing Reassurance: Offering encouragement and reassurance can alleviate anxiety and build a student’s resilience.
- Providing a Supportive Learning Environment
- Creating a Safe Space: Ensuring that students feel safe to make mistakes and ask questions fosters a positive and effective learning atmosphere.
- Encouraging Open Communication: Promoting honesty and openness helps in identifying and addressing issues promptly.
- Encouraging Persistence
- Modeling Resilience: Demonstrating perseverance in the face of challenges inspires students to adopt similar attitudes.
- Celebrating Effort: Acknowledging the effort students put into their studies, regardless of immediate outcomes, reinforces the value of persistence.
Fact: Empathetic tutors are associated with a 70% higher student satisfaction rate, leading to better learning outcomes and long-term academic success.
Organizational Skills
Strong organizational skills enable tutors to manage their time effectively, plan structured sessions, and keep track of each student’s progress, ensuring that tutoring is both efficient and effective.
- Planning and Scheduling Sessions
- Consistent Scheduling: Maintaining a regular tutoring schedule helps students build a routine and stay committed to their learning goals.
- Flexible Adaptation: Being adaptable to changes in schedule or student needs ensures that tutoring remains responsive and effective.
- Keeping Track of Student Progress
- Progress Monitoring Tools: Utilizing tools such as progress charts, assessments, and feedback forms helps in tracking improvements and identifying areas that need further attention.
- Regular Reviews: Conducting periodic reviews of a student’s performance ensures that tutoring strategies remain aligned with their evolving needs.
- Managing Resources and Materials
- Organizing Educational Materials: Keeping lesson plans, resources, and materials well-organized facilitates smooth and productive tutoring sessions.
- Utilizing Technology: Leveraging digital tools and platforms can enhance the efficiency of resource management and provide students with access to a wider range of learning materials.
Key Organizational Tools for Tutors
| Tool | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Scheduling Software | Managing tutoring sessions and appointments | Google Calendar, Calendly |
| Progress Tracking | Monitoring student performance and growth | Trello, Airtable, Excel Spreadsheets |
| Resource Management | Organizing lesson plans and educational materials | Evernote, Google Drive, Dropbox |
| Communication Platforms | Facilitating seamless communication with students and parents | Zoom, Skype, Slack |
Case Study: Streamlining Tutoring with Organizational Tools
Lucas’s Improvement in Literature
Lucas, a high school student, struggled with organizing his thoughts and writing coherent essays in his literature class. His tutor implemented a structured approach to help him develop these skills.
Tutor’s Approach:
- Structured Lesson Plans: Developed clear and organized lesson plans focusing on essay writing techniques and literary analysis.
- Progress Tracking: Utilized a progress tracking spreadsheet to monitor Lucas’s improvement in writing assignments and test scores.
- Resource Management: Provided Lucas with access to a shared Google Drive folder containing sample essays, writing prompts, and feedback forms.
Lucas became more organized in his writing process, leading to more coherent and well-structured essays. His grades improved from a B- to an A over two semesters, and he gained greater confidence in his writing abilities.
Possessing subject matter expertise, communication skills, patience and empathy, and organizational skills are fundamental to fulfilling what is my role as a tutor effectively. These skills not only enhance your ability to teach but also contribute to creating a positive and impactful learning experience for your students.