In the ever-evolving landscape of education, the diversity of teaching methods plays a pivotal role in fostering effective learning environments. As educators strive to meet the varied needs of their students, understanding and implementing different teaching strategies becomes essential. This article delves into what are the 15 methods of teaching, offering a comprehensive guide to each approach and highlighting their significance in modern education.
Education is no longer a one-size-fits-all endeavor. With the recognition that students have unique learning styles, preferences, and abilities, educators are increasingly adopting a variety of teaching methods to enhance engagement, comprehension, and retention. From traditional lectures to innovative digital techniques, the spectrum of teaching methods is vast and dynamic.
The purpose of exploring the 15 methods of teaching is to equip educators, students, and educational institutions with the knowledge to select and implement the most effective strategies. By understanding the strengths and applications of each method, teachers can create more inclusive and stimulating classrooms, while students can benefit from approaches that resonate with their individual learning styles.
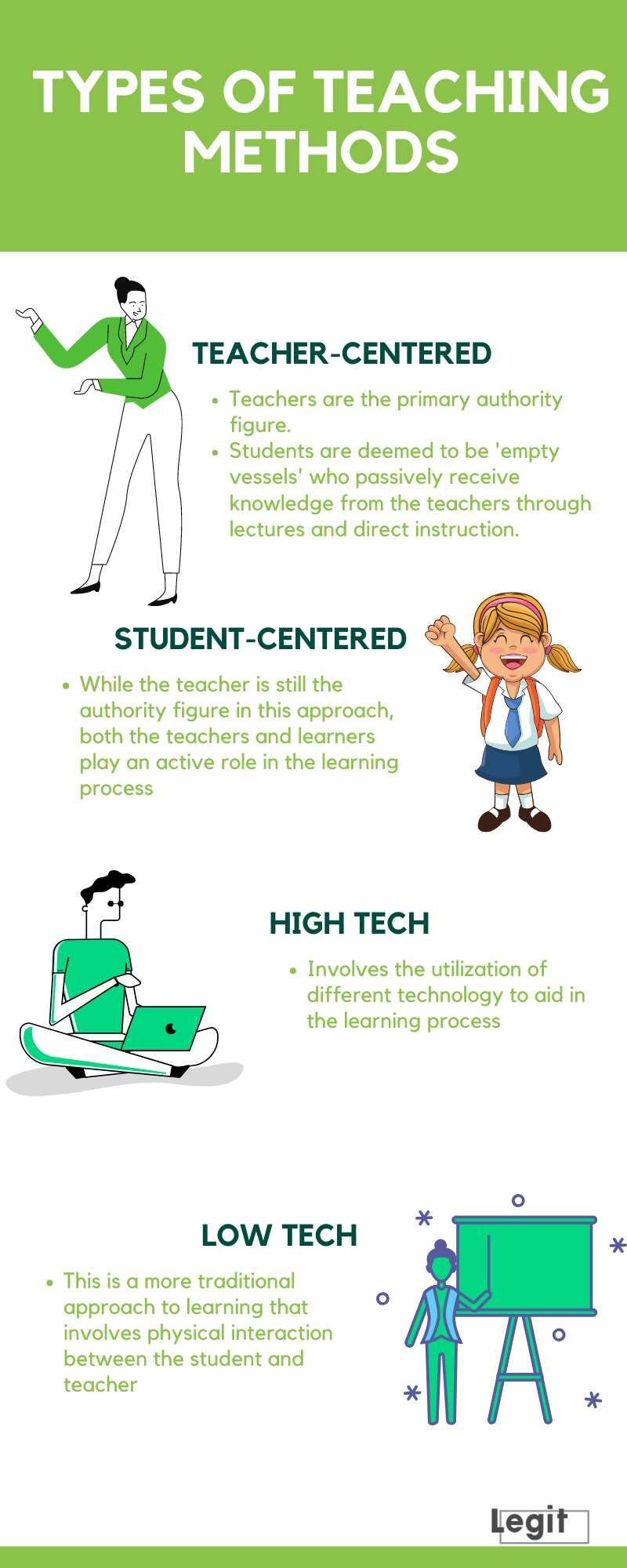
What Are Teaching Methods?
Teaching methods are the various strategies and techniques that educators use to facilitate learning and impart knowledge to students. These methods encompass a wide range of approaches, each designed to cater to different learning styles, objectives, and classroom environments. Understanding what are the 15 methods of teaching involves recognizing the diverse ways in which instruction can be delivered to maximize student engagement and comprehension.
At its core, a teaching method is the structured approach an educator takes to present information, encourage interaction, and assess understanding. Effective teaching methods are not just about the delivery of content but also about fostering an environment where students feel motivated to learn and participate actively. The choice of method can significantly impact the effectiveness of the learning process, influencing how well students grasp and retain the material.
Key Components of Teaching Methods:
- Instructional Strategies: These are the specific techniques used to present information, such as lectures, discussions, or hands-on activities.
- Learning Activities: These involve the tasks students engage in to process and apply what they’ve learned, like group projects, experiments, or case studies.
- Assessment Techniques: Methods used to evaluate student understanding and progress, including quizzes, essays, and presentations.
Importance of Selecting Appropriate Teaching Methods:
- Enhances Learning Outcomes: Different methods cater to various learning styles—visual, auditory, kinesthetic—ensuring that all students have the opportunity to excel.
- Increases Engagement: Interactive and varied teaching methods can make learning more interesting and relevant, reducing boredom and increasing participation.
- Addresses Diverse Needs: Classrooms are often composed of students with diverse backgrounds and abilities. A variety of teaching methods can help meet these diverse needs effectively.
- Promotes Critical Thinking: Methods like the Socratic approach or problem-based learning encourage students to think deeply and critically about the subject matter.
Impact on Student Learning and Engagement:
The choice of teaching method directly affects how students interact with the material and with each other. For example, cooperative learning encourages teamwork and communication, while the lecture method may be more suitable for delivering large amounts of information efficiently. By strategically selecting and combining different teaching methods, educators can create a more dynamic and responsive learning environment that fosters both academic and personal growth.
Case Study:
Consider a high school biology class where the teacher employs a mix of demonstration methods and problem-based learning (PBL). During lectures, the teacher demonstrates complex biological processes using visual aids and real-life examples, making the information more accessible. In subsequent classes, students engage in PBL by working in groups to solve real-world biological issues, such as designing sustainable ecosystems. This combination not only reinforces theoretical knowledge but also develops critical thinking and collaborative skills.
Understanding what are the 15 methods of teaching begins with a clear grasp of what teaching methods entail and their significance in the educational process. By selecting appropriate teaching methods, educators can create effective, engaging, and inclusive learning environments that cater to the diverse needs of their students.

Why Are There 15 Methods of Teaching?
Embracing Diversity in Teaching Approaches
When exploring what are the 15 methods of teaching, it’s essential to understand the rationale behind identifying and categorizing these specific methods. The diversity in teaching approaches stems from the need to address the varied learning styles, preferences, and needs of students. Education is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor, and recognizing why there are 15 methods of teaching helps educators create more effective and inclusive learning environments.
Explanation of the Diversity in Teaching Approaches
The educational landscape is influenced by numerous factors, including cultural backgrounds, technological advancements, and evolving pedagogical theories. These factors contribute to the development of a wide array of teaching methods, each tailored to enhance different aspects of the learning process. Here’s why diversity in teaching methods is crucial:
- Catering to Different Learning Styles:
- Visual Learners: Benefit from methods that incorporate images, diagrams, and videos.
- Auditory Learners: Thrive with lectures, discussions, and verbal explanations.
- Kinesthetic Learners: Prefer hands-on activities and interactive experiences.
- Addressing Varied Educational Needs:
- Students have unique strengths and areas for improvement. Diverse teaching methods ensure that all students have the opportunity to excel in ways that suit their individual needs.
- Enhancing Engagement and Motivation:
- Varied teaching approaches keep the learning experience dynamic and interesting, reducing monotony and increasing student motivation.
- Promoting Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving:
- Different methods encourage students to engage with the material in various ways, fostering critical thinking and the ability to solve complex problems.
Benefits of Having Multiple Teaching Methods
Understanding why there are 15 methods of teaching also involves recognizing the specific benefits that a variety of methods bring to the educational process:
- Flexibility in Instruction:
- Teachers can adapt their methods based on the subject matter, classroom dynamics, and specific learning objectives.
- Improved Learning Outcomes:
- Utilizing multiple methods can lead to better retention and understanding of information, as students engage with the material through different modalities.
- Inclusive Education:
- A variety of teaching methods ensures that education is accessible to all students, including those with special needs or different cultural backgrounds.
- Enhanced Teacher Effectiveness:
- Teachers who are proficient in multiple methods can better manage diverse classrooms and respond to the changing needs of their students.
- Encouragement of Lifelong Learning:
- Exposure to different teaching methods can inspire students to adopt diverse learning strategies, fostering a habit of continuous learning and adaptability.
Adapting Methods to Different Learning Styles and Environments
One of the primary reasons there are 15 methods of teaching is to allow educators to tailor their instruction to fit various learning styles and environments. Here’s how different methods align with specific settings and styles:
- Traditional Classroom Settings:
- Methods like the Lecture Method and Direct Instruction are often used in traditional classrooms where structured delivery of information is essential.
- Collaborative Environments:
- Cooperative Learning and Project-Based Learning (PjBL) thrive in environments that encourage teamwork and collaboration among students.
- Modern, Tech-Integrated Classrooms:
- Blended Learning and E-Learning methods leverage technology to create interactive and flexible learning experiences.
- Hands-On Learning Environments:
- Experiential Learning and the Montessori Method are ideal for settings that prioritize hands-on activities and real-world applications.
- Critical Thinking and Discussion-Oriented Classrooms:
- The Socratic Method and Inquiry-Based Learning foster deep thinking and open dialogue, making them suitable for discussion-driven classrooms.
The Role of Educational Context in Method Selection
The choice of teaching methods is also influenced by the educational context, including:
- Age of Students:
- Younger students may benefit more from Montessori or Cooperative Learning, while older students might engage better with Problem-Based Learning (PBL) or the Flipped Classroom model.
- Subject Matter:
- Subjects that require critical analysis, such as literature or social sciences, may utilize the Socratic Method, whereas sciences might benefit from Demonstration Methods and Experiential Learning.
- Institutional Goals:
- Schools and educational institutions often have specific goals, such as fostering creativity or enhancing technological proficiency, which can dictate the adoption of certain teaching methods.
Case Study: Implementing Multiple Teaching Methods in a Diverse Classroom
Consider a middle school classroom that embraces the 15 methods of teaching to accommodate a diverse group of students. The teacher employs the Lecture Method to introduce new topics, ensuring that all students receive foundational knowledge. To reinforce this, Cooperative Learning groups are formed, allowing students to discuss and collaborate on assignments, fostering social and communication skills.
For subjects requiring critical thinking, such as history, the teacher uses the Socratic Method to engage students in deep discussions and debates. In science classes, Experiential Learning is implemented through lab experiments, providing hands-on experience that enhances understanding.
Additionally, the teacher incorporates Blended Learning by utilizing online resources and digital tools, catering to tech-savvy students and providing flexible learning options. This comprehensive approach not only addresses the varied learning styles within the classroom but also creates a dynamic and inclusive educational environment.

How to Choose the Right Teaching Method
Selecting the Most Effective Teaching Method for Your Classroom
Choosing the right teaching method is a crucial step in creating an effective and engaging learning environment. With what are the 15 methods of teaching available, educators have a wealth of options to tailor their instruction to meet the diverse needs of their students.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Teaching Method
Selecting an appropriate teaching method involves evaluating several critical factors that influence the learning process. Here are the primary considerations:
1. Subject Matter
Different subjects lend themselves to different teaching methods. For instance:
- Mathematics and Sciences: Often benefit from the Demonstration Method and Problem-Based Learning (PBL), which allow for hands-on experimentation and real-world problem-solving.
- Humanities and Social Sciences: May be well-suited to the Socratic Method and Discussion Method, fostering critical thinking and debate.
- Languages: Can thrive with the Immersive Method and Cooperative Learning, enhancing communication and collaboration skills.
2. Learning Objectives
Clarifying what you aim to achieve with your lesson is essential. Are you focusing on:
- Knowledge Acquisition: Methods like Lecture and Direct Instruction are effective for conveying factual information.
- Skill Development: Experiential Learning and Project-Based Learning (PjBL) help students develop practical skills.
- Critical Thinking: The Socratic Method and Inquiry-Based Learning encourage deeper analysis and reasoning.
3. Student Demographics
Understanding the composition of your classroom can guide your method selection:
- Age and Developmental Stage: Younger students might benefit more from Montessori or Cooperative Learning, while older students may engage better with Flipped Classroom or Blended Learning.
- Cultural Backgrounds: Incorporating diverse methods can help address varied cultural learning preferences and promote inclusivity.
- Learning Styles and Needs: Recognizing that students have different preferences (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) ensures that the chosen methods cater to all learners.
4. Classroom Environment
The physical and technological setup of your classroom can influence method effectiveness:
- Traditional Settings: Methods like Lecture and Direct Instruction may be more practical.
- Technology-Enhanced Classrooms: Blended Learning and E-Learning methods leverage digital tools for interactive and flexible learning experiences.
- Collaborative Spaces: Cooperative Learning and Project-Based Learning (PjBL) thrive in environments that support teamwork and group activities.
5. Resources and Constraints
Available resources, including time, materials, and technology, play a significant role in method selection:
- Limited Resources: Methods that require minimal materials, such as the Lecture Method or Discussion Method, can be more feasible.
- Abundant Resources: Experiential Learning and Demonstration Method may be utilized effectively when ample materials and equipment are available.
Practical Tips for Educators
To effectively choose and implement the right teaching method, consider the following strategies:
1. Assess Student Needs and Preferences
- Surveys and Feedback: Gather information from students about their preferred learning styles and what methods they find most engaging.
- Observation: Pay attention to how students respond to different teaching approaches and adjust accordingly.
2. Align Methods with Learning Goals
- Clear Objectives: Ensure that the chosen method directly supports the learning outcomes you aim to achieve.
- Method-Goal Fit: For example, use Problem-Based Learning (PBL) when the goal is to develop problem-solving skills.
3. Combine Multiple Methods
- Blended Approaches: Integrate several teaching methods within a single lesson to address different aspects of learning. For instance, start with a Lecture to introduce a topic, followed by Cooperative Learning activities to apply the concepts.
- Flexibility: Be prepared to switch methods if a particular approach is not meeting the desired outcomes.
4. Incorporate Technology Thoughtfully
- Digital Tools: Utilize technology to enhance traditional methods. For example, use interactive whiteboards during Lectures or online collaboration platforms for Cooperative Learning.
- E-Learning Resources: Incorporate online modules and resources to complement in-person instruction, especially in Blended Learning environments.
5. Continuously Reflect and Adapt
- Self-Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your teaching methods through student performance and feedback.
- Professional Development: Stay informed about new teaching methods and pedagogical research to continually refine your approach.
Importance of Flexibility and Adaptability in Teaching
Education is a dynamic field, and the ability to adapt your teaching methods is essential for sustained effectiveness. Here’s why flexibility matters:
1. Responding to Diverse Learning Needs
Students’ needs can change over time, and being adaptable allows you to address these evolving requirements effectively. For example, integrating Differentiated Instruction can help cater to individual learning paces and styles.
2. Adapting to Technological Advances
With the rapid advancement of technology, new teaching methods emerge that can enhance learning experiences. Being open to incorporating E-Learning and other digital methods ensures that your teaching remains relevant and effective.
3. Handling Classroom Dynamics
Classroom dynamics, such as group interactions and varying levels of student participation, can influence the success of a teaching method. Flexibility allows you to modify your approach to maintain a positive and productive learning environment.
4. Overcoming Challenges
Unexpected challenges, such as disruptions or changes in curriculum, require teachers to quickly adapt their methods to continue providing quality education. Flexible educators can maintain continuity and effectiveness despite obstacles.
Case Study: Choosing the Right Teaching Method in a High School Setting
Scenario: A high school history teacher aims to enhance student engagement and critical thinking skills in a diverse classroom. The teacher decides to implement a combination of teaching methods to achieve these goals.
Approach:
- Lecture Method: Used to introduce historical events and provide foundational knowledge.
- Socratic Method: Employed during discussions to encourage critical analysis and debate on historical interpretations.
- Project-Based Learning (PjBL): Assigned projects where students create presentations or models related to historical events, fostering creativity and practical application of knowledge.
- Blended Learning: Incorporated online resources and interactive timelines to complement in-person lessons, allowing students to explore topics at their own pace.
Outcome: By thoughtfully selecting and combining these methods, the teacher successfully increased student engagement, improved critical thinking skills, and created a more interactive and inclusive learning environment. Students reported higher levels of interest and better retention of historical knowledge.